Describe How New Nucleotides Are Added During Dna Replication.
This primer is removed later and the nucleotides are replaced with DNA nucleotides. DNA replication proceed with high fidelityIn simple words it means During DNA replication deoxy ribonucleotides are added to the growing DNA strand with little or no error.

Molecular Events Of Dna Replication Learn Science At Scitable
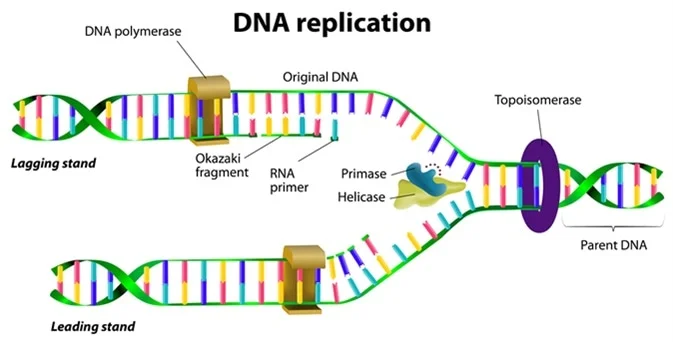
During DNA replication the enzyme DNA helicase unwinds the double helical structure by breaking the hydrogen bonds between adjacent bases of either strand.
. What do nucleotides do in DNA replication. 5 What initiates the synthesis of a new DNA strand. 2 What determines the sequence of nucleotides.
DNA itself is made up of nucleotides. The correct answer is d DNA polymerase proofreads the new DNA. During elongation in DNA replication the addition of nucleotides occurs at its maximal rate of about 1000 nucleotides per second.
A replication fork is formed which serves as a template for replication. This process occurs at several locations on a DNA molecule. Adenine pairs with thymine thymine pairs with adenine cytosine pairs.
Prior to replication the DNA uncoils and strands separate. During replication the DNA double helix unwinds to form the replication fork. DNA replication occurs in a series of five steps.
This provides one template strand for new nucleotides to be added to their complementary bases on the template strand. DNA polymerase III can only extend in the 5 to 3 direction which poses a problem at the replication fork. DNA polymerase III ATP GTP TTP CTP.
Each molecule consists of a strand from the original molecule and a newly formed strand. Lagging strand synthesis occurs in the same direction as the replication fork. How are new nucleotides added at replication fork How are new nucleotides added from BIO 310 at Cleveland State University.
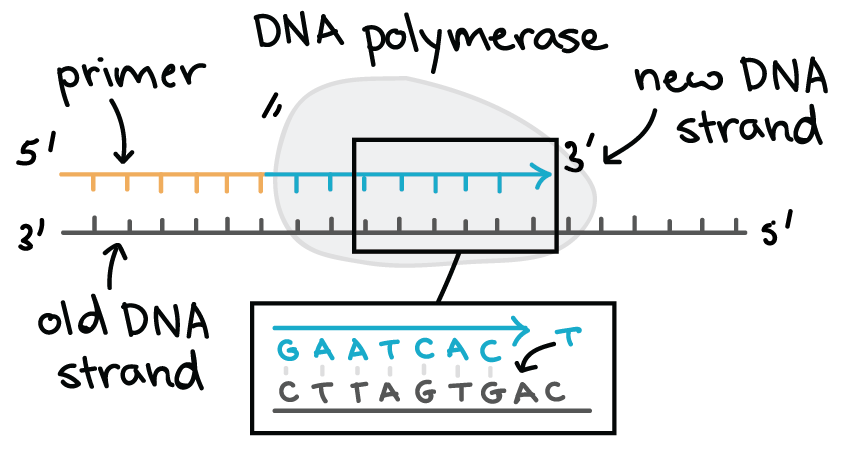
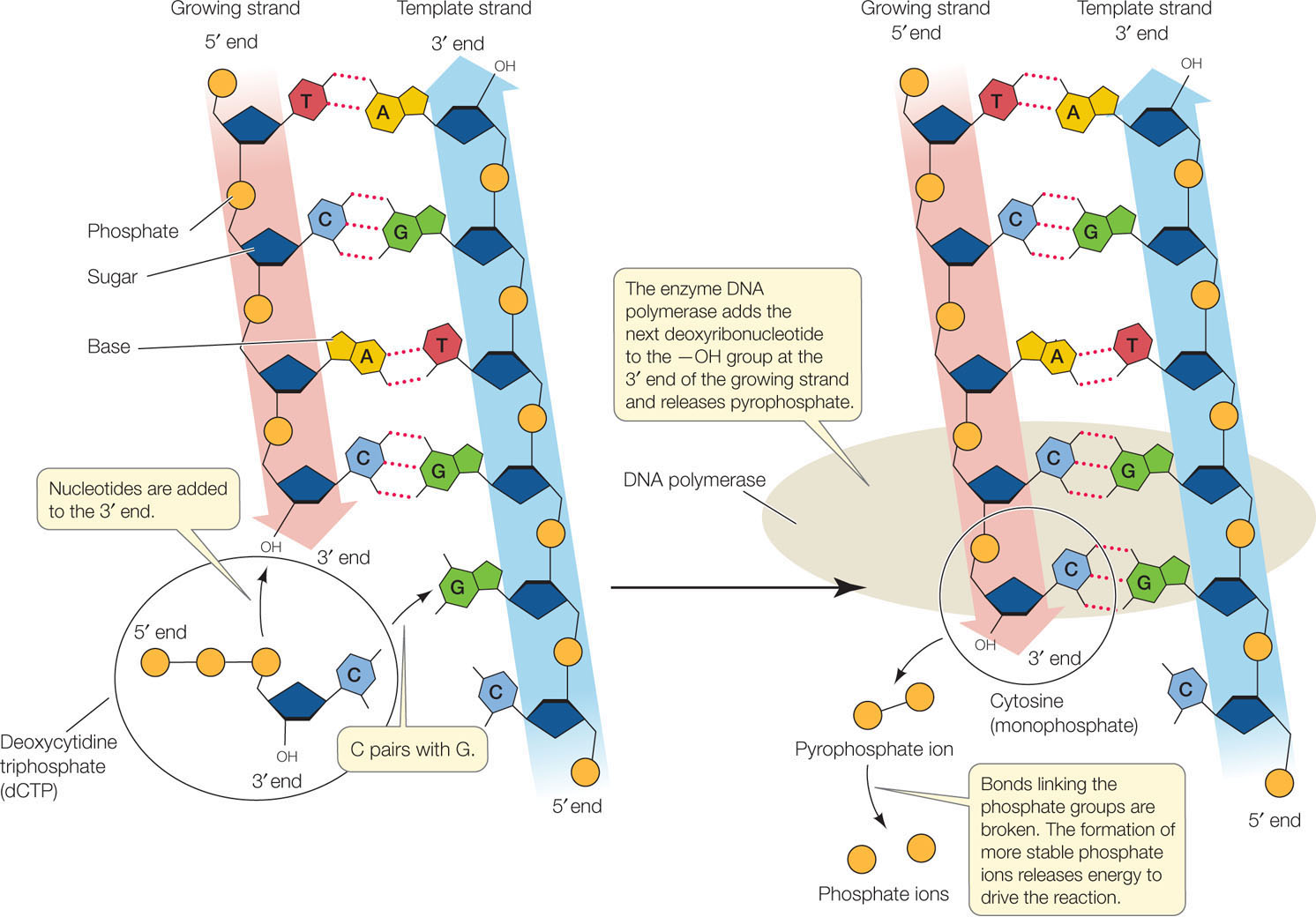
During DNA replication new nucleotides are added at the 3 end of the molecule. A hairpin forms when DNA polymerase adds new nucleotides. Nucleotides bases are matched to synthesize the new partner strands into two new double helices.
Start studying DNA Replication. The double helix is unzipped and unwound then each separated strand turquoise acts as a template for replicating a new partner strand green. Video is an animated explanation of How Nucleotides are Added in DNA Replication.
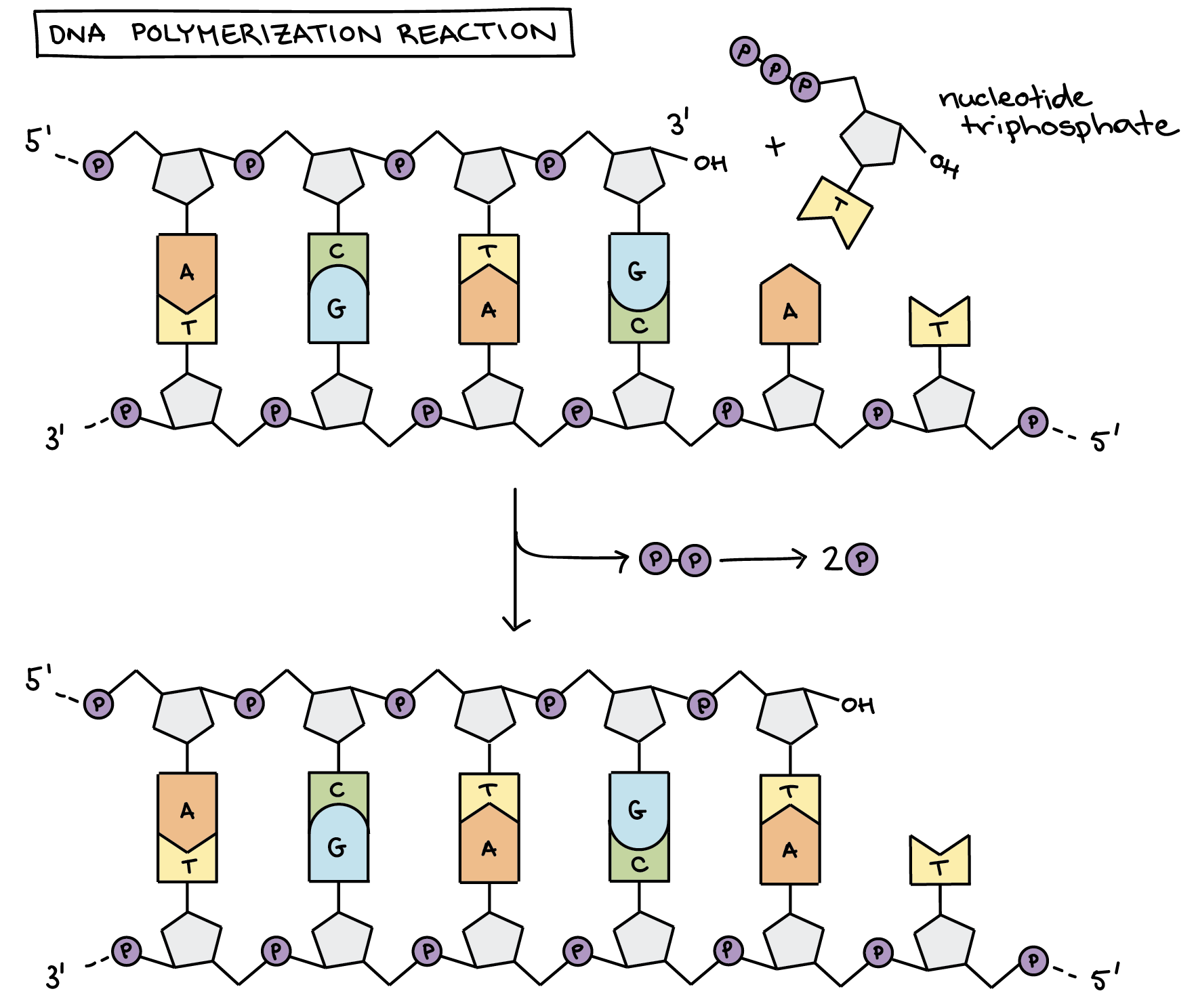
The two arms of each Y Initially the simplest mechanism of DNA replication seemed to be the continuous growth of both new strands nucleotide by nucleotide at the replication fork as it moves from one end of a DNA molecule to. Energy of Replication The nucleotides arrive as nucleosides DNA bases with PPP P-P-P energy for bonding DNA bases arrive with their own energy source for bonding bonded by enzyme. The trinucleotide regions are replicated during two rounds of replication but will not be replicated again once round two is completed DNA polymerase slipping results from the presence of the trinucleotide repeat.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The trinucleotide regions are replicated with each round of replication and therefore get longer over.
Initiation at the origin of replication unwinding to expose the strands synthesis on both strands with many enzymes adding nucleotides 3 to 5 lengthening by RNA primers and separation into two complete molecules. In the process of DNA replication parent DNA strand needs to be duplicated. This means that one strand has a series of breaks in the sequence.
In the leading strand DNA polymerase can add nucleotides continuously and the growth of the new. 4 What strand is synthesized during DNA replication. Next to the box using two different colored penspencil create two new strands from the original strand in the box A.
Therefore we call this strand as the leading strand. Leading strand synthesis occurs continuously. 1 See answer.
Okazaki fragments remain in the DNA. That is one strand is oriented in the 5 to 3 direction and the other is oriented in the 3 to 5. Label which color represents the original.
DNA replication is the production of identical DNA helices from a single double-stranded DNA molecule. Because DNA polymerase can only add new nucleotides at the end of a backbone a primer sequence which provides this starting point is added with complementary RNA nucleotides. Primers bind to the DNA and DNA.
The DNA double helix is antiparallel. In bacteria DNA polymerase lays down the RNA primer. Each other to form a DNA chain.
DNA polymerase adds the free DNA nucleotides to the 3 end of the primer. 3 How would you tell which DNA strand is newly synthesized. So this one works really well to just build five prime 23 prime but in the other direction we have to go in the opposite way because the five prime end is going to be over.
AnswerDNA replication goes in the 5 to 3 direction because DNA polymerase acts on the 3-OH of the existing strand for adding free nucleotidesExplanation. Stage two DNA polymerase will add the free DNA nucleotides using complementary base. An active zone of DNA replication moves progressively along a replicating DNA molecule creating a Y-shaped DNA structure known as a replication fork.
Clarissamaebowers clarissamaebowers 11172019 Biology Middle School answered Which direction are new nucleotides added during replication. This uses complementary base pairing A-T and C-G. So on this new strand here were going to build in this direction working well with the replication fork here because were going to keep opening this more and more as the D N A travels through replication.
The whole process occurs in the nucleus and is 1000 times faster than RNA transcription. Here the DNA strand which opens up in the 3 to 5 direction allows the growth of the strand continuously in the 5 to 3 direction. One strand which is complementary to the parental DNA strand is synthesized continuously toward the.
The purine base adenine and the pyrimidine base thymine form two hydrogen bonds. 1 What Determines The Nucleotide Sequence Of The Newly Synthesized Strand During Dna Replication. In the box A below fill in the complementary strand of DNA to create a double strand.
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy

Dna Replication Steps Diagram Expii
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy

Molecular Events Of Dna Replication Learn Science At Scitable
9 2 Dna Replication Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition


0 Response to "Describe How New Nucleotides Are Added During Dna Replication."
Post a Comment